搜索结果: 1-13 共查到“土壤学 NO”相关记录13条 . 查询时间(0.171 秒)

中国南方亚热带森林土壤中长期高的大气氮沉降导致其成为气态氮(一氧化氮(NO)和氧化亚氮(N2O))释放的热点区域。土壤湿度是NO和N2O释放速率的主要控制因子,尤其在具有季风气候,干湿交替频繁的亚热带森林。然而,土壤湿度对中国亚热带森林土壤NO周转和N2O释放的具体调控作用及其过程机理,目前知之甚少。
【目的】 研究一氧化氮 (NO) 对镉 (Cd) 胁迫下水稻苗期生理生化及氮代谢响应的调节作用,探讨通过清除NO提高水稻耐Cd能力的措施。 【方法】 以Cd高积累 (TN1) 和Cd低积累 (春江06) 品种为材料,进行了Cd胁迫 (40 μmol/L) 水培试验。以Cd胁迫营养液为对照,在对照基础上设置添加硝普钠 (Cd+SNP)、添加NO清除剂CPTIO (Cd+CPTIO)、添加...
北京设施菜地N2O和NO排放特征及滴灌优化施肥的减排效果
设施菜地 滴灌施肥 优化施肥 N2O和NO排放
2019/8/7
【目的】量化设施菜地N2O、NO排放特征,分析其影响因素,以期为科学评估农田生态系统N2O、NO排放提供关键参数。【方法】以黄瓜品种‘金胚98’为供试材料,在北京房山区窦店乡的温室大棚内进行了田间试验,供试土壤类型为石灰性褐土,质地为壤土。试验共设4个处理:漫灌,不施氮肥 (CK);漫灌,农民习惯施肥 (FP);滴灌,农民习惯施肥 (FPD);滴灌,优化施氮 (OPTD)。常规氮肥施用量为N 12...
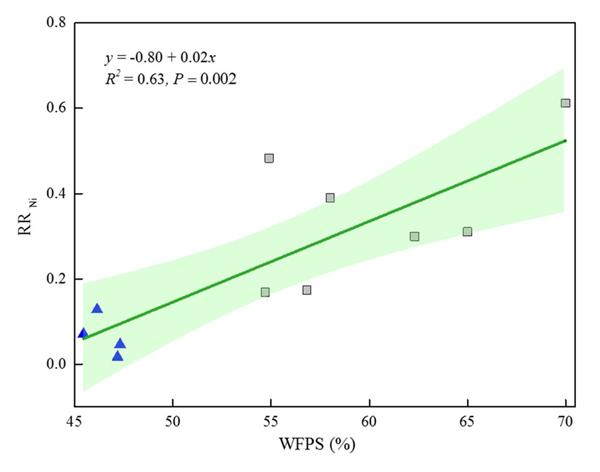
中国科学院南京土壤研究所丁维新课题组采用田间小区试验,研究了生物质炭和抑制剂对华北平原潮土N2O和NO的影响。试验包括9个处理:不施氮肥(control)、单施化肥(N)、化肥+3 ton ha-1生物质炭(NB3)、化肥+6 ton ha-1生物质炭(NB6)、化肥+12 ton ha-1生物质炭(NB12)、N+硝化抑制剂、NB3+硝化抑制剂、NB6+硝化抑制剂和NB12+硝化抑制剂。生物质炭...
Biological potential and diffusion limitation of methane oxidation in no-till soils
methane oxidation in no-till soils Biological potential
2015/1/16
Long term no-till (NT) farming can improve the CH4 oxidation capacity of agricultural lands through creation of a favorable soil environment for methanotrophs and diffusive gas transport. However, lim...
利用15N同位素标记方法,研究在两种水分条件即60%和90% WHC下,添加硝酸盐(NH4NO3,N 300mgkg-1)和亚硝酸盐(NaNO2,N 1mg kg-1)对中亚热带天然森林土壤N2O和NO产生过程及途径的影响。结果表明,在含水量为60% WHC的情况下,高氮输入显著抑制了N2O和NO的产生(p < 0.01);但当含水量增为90% WHC后,实验9h内抑制N2O产生,之后转为促进。所...
为探讨外源NO(SNP为供体)对50 μmol/L铜、镉毒害的缓解效应,采用营养液培养方法,研究了不同程度的铜、镉毒害(5 μmol/L和50 μmol/L)对番茄幼苗生物量、根系活力、硝酸还原酶、光合特性及生物膜ATPase、H+-PPase等功能蛋白酶活性的影响。结果表明,铜、镉胁迫显著抑制番茄生长。随处理浓度增加,番茄根系活力、硝酸还原酶活性显著降低,番茄长势越差; 铜、镉胁迫对根系离子吸收...
采用营养液培养,研究了外源一氧化氮(NO)供体硝普钠(Sodium nitroprusside, SNP)对50 μmol/L铜(Cu)胁迫下番茄叶片叶绿素含量、光合特性、生物发光强度和矿质营养元素的影响。结果表明,在Cu胁迫下,外施100 μmol/L SNP显著提高番茄叶片叶绿素a、叶绿素b、叶绿素a+b含量、叶绿素a/b比值、净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)和叶片中Cu...
不同基肥施用方式及用量对冬小麦田NO 排放通量的影响
冬小麦 NO 排放通量 施肥方式
2009/4/10
用静态箱法对冬小麦不同基肥施用方式( 表施、深施) 和不同施用量下的土壤NO 排放通量进行了研究, 结果表明: 肥料在土壤中
的位置对NO 排放通量的影响非常显著。表施处理明显促进NO 的排放, 表施处理平均比深施处理NO 排放量高2 .2 倍。高肥处理总的
NO 排放量也明显高于低肥处理。由此可知肥料深施和减少用量都能显著降低NO 排放量。
Phosphorus and Potassium Fertilization of Disk-Till and No-Till Cotton
Phosphorus Potassium Fertilization Disk-Till No-Till Cotton
2008/12/9
Conservation-tillage practices have renewed interest in research evaluating fertilization responses of cotton. Research was conducted to evaluate the cotton-yield response to P and K fertilization und...
Winter Annual Cover Crops in a Virginia No-till Cotton Production System: II. Cover Crop and Tillage Effects on Soil Moisture, Cotton Yield, and Cotton Quality
Virginia No-till Cotton Production Winter Annual Cover Crops
2008/5/19
Winter annual cover crops could help control soil erosion problems on sloping Piedmont soils in a no-till cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) production system. Field experiments were conducted from 1995 t...
Winter Annual Cover Crops in a Virginia No-till Cotton Production System: I. Biomass Production, Ground Cover, and Nitrogen Assimilation
Virginia No-till Cotton Winter Annual Cover Crops
2008/5/13
Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) may not provide sufficient surface residue to reduce erosion and protect the soil between crops. A winter annual cover crop might alleviate erosion during the time betwe...
Potassium Fertilization of Conventional- and No-Till Cotton
Conventional- and No-Till Cotton Potassium Fertilization
2008/5/12
Potassium fertilization meeting the uptake requirements of the fast-fruiting cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars requires information on soils of varying extractable K levels, tillage systems, an...

